Since 2003, Textkernel has been transforming job posting data into actionable intelligence through what is now known as Market IQ.
Powered by advanced AI and deep labor market expertise, Market IQ delivers unmatched insights into hiring trends, in-demand skills, and emerging job roles across 15 countries: Austria, Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, the United Kingdom, United States, and more.
Whether you’re in Corporate HR, building HR Tech providers, or running a job board, Market IQ helps you stay ahead of the curve with the data you need to make smarter, faster decisions.
The unique aspects of Labor Market Insights:
- A very large number of sources (thousands of websites) that are spidered daily
- Detailed enrichment on the job information that allows the use of many search criteria, regardless of the structure of the original vacancy text
- A high quality and reliable discovery and extraction process, resulting from years of experience
- Accurate deduplication of job postings
- Coding of professions and other criteria to customer-specific taxonomies
- Customised reporting
- An unprecedented history of job data for analysis purposes and the capacity to make these jobs analysable with new insights
Labor Market Insights provides the ability to draw a near real-time picture of the labour market, and creates the opportunity to do trend analysis based on historic information from its large job database.
The process
Labour Market Insights tool searches the Internet daily for new jobs via an automated process. Found jobs are automatically extracted, categorised and recorded in the Market IQ database. The following diagram shows a schematic representation of this process.
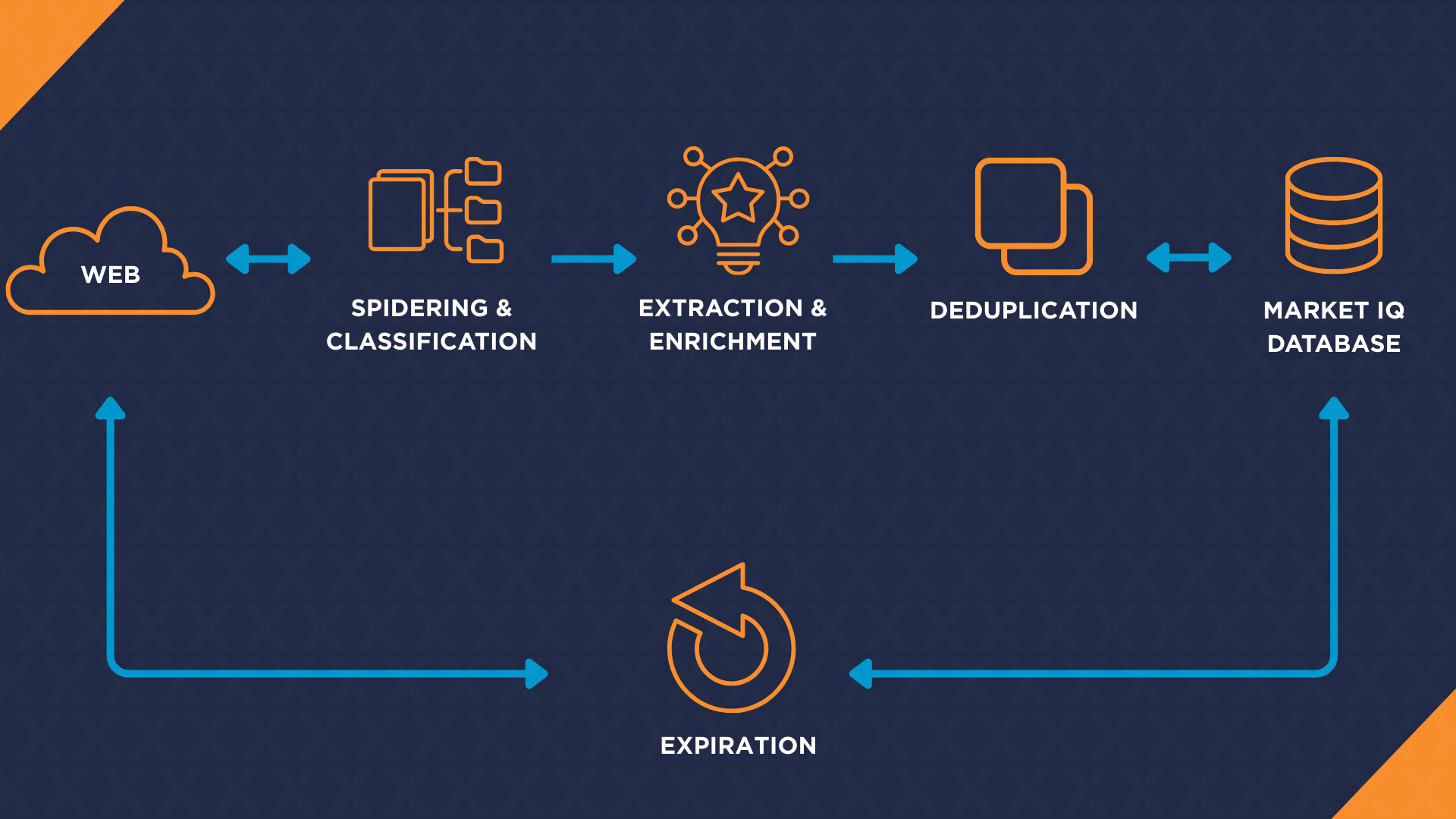
Spidering
Labor market insights obtains new jobs from the Internet daily through spidering. In order to achieve broad and deep coverage, Market IQ uses two spider methods: wild spidering and targeted spidering.
The wild spider is a system that works automatically and dynamically. It continuously indexes hundreds of thousands of relevant (company) websites and discovers new job postings.
Targeted spider scripts are created to retrieve jobs from specific – usually large – websites, like job boards, and websites of large employers. Despite their size and complexity, the script ensures that all jobs are found. The targeted spider scripts run multiple times per day.
Additionally, Labor market insights searches Twitter for links to jobs (currently only in The Netherlands).
Job sites that only copy or repost jobs from other sites (so-called aggregators), are excluded from Labor market insights , because Market IQ already indexes the original jobs. Furthermore, aggregators often lose or misinterpret important information from the original job, resulting in bad quality.
Classification
Classification involves determining whether a retrieved web page contains a job or not. By means of advanced language technology and using textual features on the page, Textkernel’s algorithm determines whether the page should be processed. The classification is tuned to accept as many jobs as possible while discarding as many pages as possible that are not jobs.
Classification is only needed for pages coming from the wild spider, because the targeted spider scripts only fetch pages that are known to contain jobs.

Information extraction
In order to make the jobs searchable, they are automatically structured by means of Textkernel’s intelligent information extraction software. This software is trained on finding data in free text and is therefore independent of the structure of the text or format of the source.
The extraction process consists of two steps:
1. Cleaning the web page, by removing all non-relevant content (such as menus and forms), leaving only the actual job text. In case of PDF input, this step does not apply.
2. Extracting and validating more than 30 fields from the text, such as job title, location, education level and organisation.
Normalisation and enrichment
Normalisation means that extracted data is categorized according to a standard format. This makes it easier to search the data and perform analyses. Normalisation takes place on fields like professions, education levels and organisations.
For example, normalisation of professions is done by means of a taxonomy. This is a hierarchal structure that consists of reference professions with synonyms. The extracted position title is matched to one of the synonyms. The match does not need to be exact. The job will be linked to the most similar profession. When searching for jobs for a certain profession, all jobs matching any of the synonyms for that profession will be found.
Enrichment is done in case of organisations. The extracted contact information from the job is used to find the corresponding record in a national company database (such as Chamber of Commerce table in The Netherlands). Because the information in the job is usually sparse, a technique called “fuzzy matching” is used. Using this technique, Labor market insights can find the right organisation, regardless of differences in spelling of organisation name, address or in case of incomplete information. From the company database other information can be derived, such as the amount of employees, the company’s primary activity and its full contact information.
Deduplication
Jobs are often posted on multiple websites, or multiple times on the same website. Deduplication is done by comparing a new job with all jobs that have been found by Market IQ in the past six weeks.
Two job postings that are duplicates of each other, are usually not identical. Deduplication therefore requires a sophisticated approach. As with the classification and extraction, the deduplication system uses a machine learning algorithm. To determine whether two jobs are duplicates of each other, the job description and important features of the job are compared, such as job title, city and advertiser.
Duplicates are not discarded, but also saved in Market IQ. This way, Market IQ is able to show not only how many unique jobs there are, but also how many job postings there have been
Expiration
Each job posting’s original source is regularly revisited to check whether it is still active. “Expired” means that the job is no longer directly available from the original URL, or that the job is no longer retrievable by a normal user from the homepage of the original website. The expiration date is stored in the Market IQ database.
Quality control
Automatic processes for spidering, extraction, classification and normalisation are the only cost-effective way to realise a maximum potential from online job data. However, these processes are not error-free. The quality of Market IQ data is continuously monitored and improved. This is done using a combination of automatic alerting and manual quality checks.


